Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (1): 106-111.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.01.018
Previous Articles Next Articles
Transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells affects the proliferation and function of CD4+T cells in mice
Su Shao-hong1,2, Zhang Jun-feng2, Li Qian-ru1, Guan Sha-sha1, Du Ying1
- 1Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Basic Medical School, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450001, Henan Province, China
2Department of Clinical Laboratory, the Fifth Affiliated Hospital, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China
-
Revised:2013-10-12Online:2014-01-01Published:2014-01-01 -
Contact:Du Ying, M.D., Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Basic Medical School, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450001, Henan Province, China -
About author:Su Shao-hong, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Basic Medical School, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450001, Henan Province, China; Department of Clinical Laboratory, the Fifth Affiliated Hospital, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81172874
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Su Shao-hong, Zhang Jun-feng, Li Qian-ru, Guan Sha-sha, Du Ying . Transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells affects the proliferation and function of CD4+T cells in mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(1): 106-111.
share this article
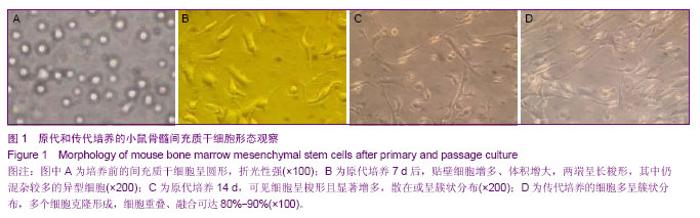
2.1 纳入实验动物数量分析 30只C57BL/6受体小鼠均分为3组,每组10只,实验过程中无脱失,均进入结果分析。 2.2 骨髓间充质干细胞体外扩增和形态 原代分离的骨髓间充质干细胞呈圆形,折光性强(图1A)。体外培养24 h可见呈圆形、胞体较小,培养三四天后可见部分细胞贴壁,呈梭形,折光性较强。培养7-10 d贴壁细胞增多、体积增大,两端长出较长突起呈长梭形,其中仍混杂有较多的异型细胞(图1B)。培养2周可见呈梭形的骨髓间充质干细胞显著增多,散在或呈簇状分布(图1C)。3周左右可见骨髓间充质干细胞多呈簇状分布,多个细胞克隆形成,细胞重叠、融合可达80%-90%(图1D)。消化传代后继续培养,细胞生长速度逐渐增快,细胞数量成倍增加。以传三四代的细胞为移植细胞(小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞)。"
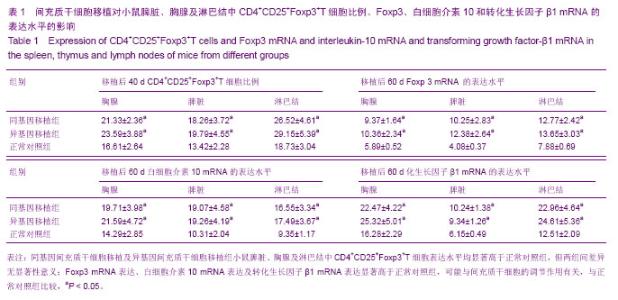
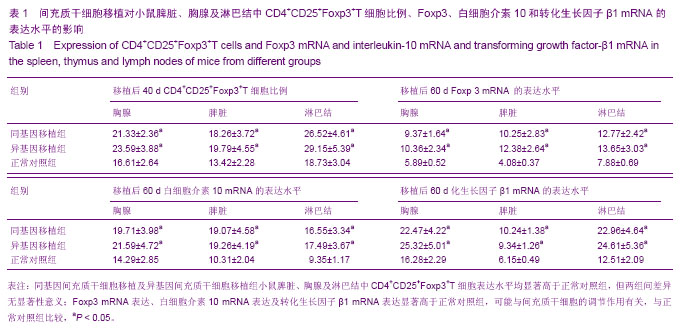
2.3 间充质干细胞移植对小鼠脾脏、胸腺及淋巴结中CD4+CD25+Foxp3+T细胞比例的影响 流式细胞结果显示正常小鼠脾脏、胸腺及淋巴结中CD4+CD25+ Foxp3+T细胞表达水平较低,同基因间充质干细胞移植及异基因间充质干细胞移植组小鼠脾脏、胸腺及淋巴结中CD4+CD25+ Foxp3+T细胞表达水平均显著高于正常对照组(P < 0.05),同基因移植组与异基因移植组小鼠脾脏、胸腺及淋巴结中CD4+CD25+Foxp3+T细胞表达水平相比较,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)(表1)。 2.4 间充质干细胞移植后小鼠脾脏、胸腺及淋巴结中Foxp3、白细胞介素10和转化生长因子β1 mRNA的表达水平 荧光定量PCR结果显示:正常对照组小鼠脾脏、胸腺及淋巴结中Foxp3、白细胞介素10和转化生长因子β1的mRNA表达水平较低且稳定。前期预实验显示,骨髓间充质干细胞在移植后20 d同基因移植组和异基因移植组小鼠脾脏、胸腺及淋巴结中Foxp3、白细胞介素10和转化生长因子β1的mRNA表达水平较低且与正常对照组比较,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。实验观察细胞移植40 d时,同基因移植组和异基因移植组中3种因子mRNA水平均升高,而移植后60 d时,同基因移植组和异基因移植组中3种因子mRNA水平均持续升高并显著高于正常对照组(P < 0.05)。 "
| [1] Nicholas R, Rashid W. Multiple sclerosis. Am Fam Physician. 2013;87(10):712-713. [2] Sosa RA, Forsthuber TG. The critical role of antigen-presentation-induced cytokine crosstalk in the central nervous system in multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011;31(10):753-768.[3] Mannie MD, Norris MS. MHC class-II-restricted antigen presentation by myelin basic protein-specific CD4+T cells causes prolonged desensitization and outgrowth of CD4- responders. Cell Immtm01. 2001;212(1):51-62.[4] Niino M. Recent prognosis on etiology and pathophysiology of multiple sclerosis. Nihon Rinsho. 2013;71(5):807-810.[5] Shahin A, Mahmoud TA, Lukic ML. Transforming growth factor beta and interferon gamma modulate the development of TH-l-mediated autoimmunity in susceptible and resistant strains of rats. Transplant Proe. 1995;27(2):1535-1536.[6] Kroenke MA, Segal BM. Thl7 and Thl responses directed against the immunizing epitope, as opposed to secondary epitopes, dominate the autoimmune repertoire during relapses of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neurosei Res. 2007;85(8):1685-1693.[7] Kom T, Anderson AC, Bettelli E, et al. The dynamics of effector T cells and Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in the promotion and regulation of autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol. 2007;191(1-2):51-60.[8] McQualter JL, Bernard CC. Multiple sclerosis: a battle between destruction and repair. J Neurochem. 2007;100(2): 295-306.[9] Mo C, Chearwae W, O'Malley JT, et al. Stat4 isoforms differentially regulate inflammation and demyelination in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 2008; 181(8):5681-5690.[10] Prigione I, Benvenuto F, Bocca P, et al. Reciprocal interactions between human mesenchymal stem cells and gammadelta T cells or invariant natural killer T cells. Stem Cells. 2009;27(3):693-702.[11] Corcione A, Benvenuto F, Ferretti E, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate B-cell functions. Blood. 2006;107(1):367-372.[12] The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Guidance Suggestions for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 2006-09-30. [13] 中华人民共和国科学技术部. 关于善待实验动物的指导性意见. 2006-09-30.[14] Dazzi F, Ramasamy R, Glennie S, et al. The role of mesenchymal stem cells in haemopoiesis. Blood Rev. 2006; 20(3):161-171.[15] Chen QQ, Yan L, Wang CZ, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells alleviate TNBS-induced colitis by modulating inflammatory and autoimmune responses. World J Gastroenterol. 2013; 19(29):4702-4717.[16] Harris VK, Faroqui R, Vyshkina T, et al. Characterization of autologous mesenchymal stem cell-derived neural progenitors as a feasible source of stem cells for central nervous system applications in multiple sclerosis. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2012;1(7):536-547.[17] Hayashi E, Hosoda T. Therapeutic application of cardiac stem cells and other cell types. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013: 736815.[18] Shi Y, Hu G, Su J,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells: A new strategy for immunosuppression and tissue repair. Cell Res 2010;20(5):510-518.[19] 于洋,邵秉,帅逸,等.骨髓间充质干细胞Fas/FasL介导的免疫调节在结肠炎治疗中的作用[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2013, 29(10):1028-1031.[20] 王月,牛坚.同种大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞诱导调节性B淋巴细胞的免疫负调节作用[J].中华器官移植杂志,2013,34(7):428- 431.[21] 贾喆,张晓敏,赵少贞,等.间充质干细胞对异体角膜移植大鼠CD4~+CD25~+Foxp3~+调节性T细胞水平的影响[J].眼科新进展,2012,32(4):301-304.[22] 罗小雨,刘海林. 骨髓间充质干细胞的免疫调节功能及其在治疗肝脏疾病中的应用[J]. 中华消化杂志,2013,33(9):643-645.[23] Anker PS, Noort WA, Kruisselbrink AB, et al. Nonexpanded primary lung bone marrow-derived mesenchymal cells promote the engraftment of umbilical cord blood-derived CD34+ cells NOD/SCID mice. Exp Hematol .2003;31(10): 881-889.[24] Wang Q, Liu T, Zhang Y,et al. Immunomodulatory effects of human placental-derived mesenchymal stem cells on immune rejection in mouse allogeneic skin transplantation. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013;27(7): 775-780. [25] 刘莹,侯宗柳.间充质干细胞移植治疗多发性硬化的研究进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2012,16(10):1889-1892.[26] 顾菲,张华勇,王红,等.间充质干细胞移植治疗多发性硬化一例[J]. 中华医学杂志,2009,89(17):1224-1224.[27] Selmani Z, Naji A, Zidi I, et al. Human leukocyte antigen-G5 secretion by human mesenchymal stem cells is required to suppress T lymphocyte and natural killer function and to induce CD4+CD25highFOXP3+ regulatory T cells. Stem Cells. 2008;26(1):212-222. [28] Prigione I, Benvenuto F, Bocca P, et al. Reciprocal interactions between human mesenchymal stem cells and gammadelta T cells or invariant natural killer T cells. Stem Cells. 2009;27(3):693-702.[29] Najar M, Raicevic G, Jebbawi F, et al. Characterization and functionality of the CD200-CD200R system during mesenchymal stromal cell interactions with T-lymphocytes. Immunol Lett. 2012;146(1-2):50-56. [30] Uccelli A, Prockop DJ.Why shouldmesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) cure autoim-mune diseases? Curr Opin Immunol. 2010;22(6):768-774.[31] Wu T, Zhang L, Xu K, et al. Immunosuppressive drugs on inducing Ag-specific CD4(+)CD25(+)Foxp3(+) Treg cells during immune response in vivo. Transpl Immunol. 2012; 27(1):30-38.[32] Yang H, Zhang Y, Wu M, et al. Suppression of ongoing experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis by transfer of RelB-silenced bone marrow dentritic cells is associated with a change from a T helper Th17/Th1 to a Th2 and FoxP3+ regulatory T-cell profile. Inflamm Res. 2010;59(3):197-205.[33] Zuo D, Liu X, Shou Z, et al. Study on the interactions between transplanted bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and regulatory T cells for the treatment of experimental colitis. Int J Mol Med. 2013;32(6):1337-1344. [34] Maccario R, Podesta M, Moretta A, et al. Interaction ofhuman mesenchymal stem cells with cells involved in alloantigen-specific immune response favors the differentiation of CD4+ T-cell subsets expressing a regulatory/ suppressive phenotype. Haematologica.2005;90(4):516-525.[35] Krampera M, Glennie S, Dyson J, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells inhibit the response of naive andmemory antigen-specific T cells to their cognate peptide. Blood. 2003;101(9):3722-3729.[36] Yi T, Song SU. Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells and their therapeutic applications. Arch Pharm Res. 2012;35(2):213-221.[37] Nasef A, Chapel A, Mazurier C, et al. Identification of IL-10 and TGF-beta transcripts involved in the inhibition of T-lymphocyte proliferation during cell contact with human mesenchymal stem cells. Gene Expr. 2007;13(4-5):217-226.[38] Batten P, Sarathchandra P, Antoniw JW, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells induce T cell anergy and downregulate T cell allo-responses via the TH2 pathway: relevance to tissue engineering human heart valves. Tissue Eng. 2006;12(8):2263-2273.[39] Rodgers JM, Miller SD. Cytokine Control of Inflammation and Repair in the Pathology of Multiple Sclerosis. Yale J Biol Med. 2012;85(4):447-468.[40] Schmetterer KG, Neunkirchner A, Pickl WF. Naturally occurring regulatory T cells:markers,mechanisms, andmanipulation. FASEB J. 2012;26(6):2253-2276.[41] 徐敏,路希敬,丁慧芳,等.输注间充质干细胞治疗小鼠原发性免疫性血小板减少症的疗效观察及机制研究[J].中华器官移植杂志, 2013,34(8):494-497.[42] 安润,杜占慧,阎慧芝.间充质干细胞治疗移植物抗宿主病的研究进展[J]. 疑难病杂志,2013,12(9):733-736.[43] Park SA, Reilly CM, Wood JA, et al. Safety and immunomodulatory effects of allogeneic canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells transplanted into the region of the lacrimal gland, the gland of the third eyelid and the knee joint. Cytotherapy. 2013;15(12):1498-1510.[44] Bocelli-Tyndall C, Bracci L, Schaeren S, et al. Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and chondrocytes promote and/or suppress the in vitro proliferation of lymphocytes stimulated by interleukins 2, 7 and 15. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009; 68(8):1352-1359.[45] Lum LG, Thakur A, Liu Q, et al. CD20-targeted T cells after stem cell transplantation for high risk and refractory non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013; 19(6):925-933.[46] Liu L, Wang Y, Fan H, et al. MicroRNA-181a regulates local immune balance by inhibiting proliferation and immunosuppressive properties of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells. 2012;30(8):1756-1770.[47] Wong CK, So WY, Law SK, et al. Estrogen controls embryonic stem cell proliferation via store-operated calcium entry and the nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT). J Cell Physiol. 2012;227(6):2519-2530.[48] Chen S, Wu H, Klebe D, et al. Regulatory T cell in stroke: a new paradigm for immune regulation. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013;2013:689827. [49] Qu N, Xu M, Mizoguchi I, et al. Pivotal Roles of T-Helper 17-Related Cytokines, IL-17,IL-22, and IL-23, in Inflammatory Diseases. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013;2013:968549.[50] Murphy AC, Lalor SJ, Lynch MA,et al. Infiltration of Th1 and Th17 cells and activation of microglia in the CNS during the course of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Brain Behav Immun. 2010;24(4):641-651. |
| [1] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [2] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [3] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [4] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [5] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [6] | Liao Chengcheng, An Jiaxing, Tan Zhangxue, Wang Qian, Liu Jianguo. Therapeutic target and application prospects of oral squamous cell carcinoma stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [7] | Xie Wenjia, Xia Tianjiao, Zhou Qingyun, Liu Yujia, Gu Xiaoping. Role of microglia-mediated neuronal injury in neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [8] | Li Shanshan, Guo Xiaoxiao, You Ran, Yang Xiufen, Zhao Lu, Chen Xi, Wang Yanling. Photoreceptor cell replacement therapy for retinal degeneration diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [9] | Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli. Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [10] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [11] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [12] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [13] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [14] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [15] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||